Breadcrumb
Radiomics for Lung Cancer Risk Assessment
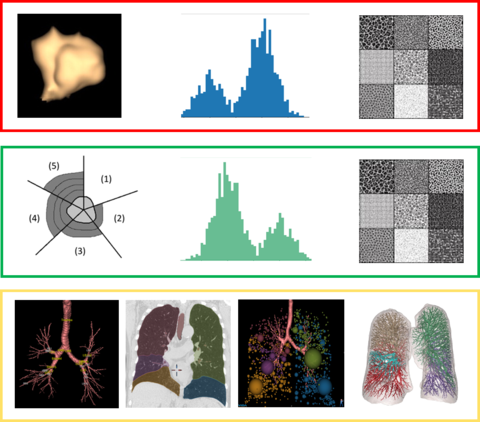
We aim to increase the efficacy of lung cancer screening with low dose computed tomography (LDCT) by developing methods to accurately predict risk of lung cancer and/or progressive obstructive lung disease at the time of screening. Our approach will focus on objective biomarkers: LDCT derived radiomic biomarkers of lung structure and an epigenetic biomarker of smoking exposure.
We have generated very promising preliminary results indicating radiomic features from CT combined with machine learning can inform non-invasive cancer risk assessment.
Schroeder KE, Acharya L, Mani H, Furqan M, Sieren JC. Radiomic biomarkers from chest computed tomography are assistive in immunotherapy response prediction for non-small cell lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023 May 31;12(5):1023-1033. doi: https://doi.org/10.21037/tlcr-22-763 Epub 2023 May 11. PMID: 37323179; PMCID: PMC10261870.
Knoernschild K, Schroeder K, Kitzmann J, Colby C, Sieren JC. Ensemble Artificial Neural Network Lung Nodule Classification Utilizing Nodular and Peri-Nodular Radiomics. Proc. SPIE 13407, Medical Imaging 2025: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, 134072K (4 April 2025); https://doi.org/10.1117/12.3047009
Uthoff J, Stephens MJ, Larson JS, Koehn N, De Stefano FA, Lusk C, Wenzlaff AS, Watza D, Neslund-Dudas C. Lynch DA, Newell Jr. JD, Schwartz AG, Sieren JC. Machine learning approach for distinguishing malignant and benign lung nodules utilizing standardized perinodular parenchymal features from CT. Medical Physics 2019. Jul;46(7):3207-3216 Epub 2019/05/16. doi: 10.1002/mp.13592. PubMed PMID: 31087332; PMCID: PMC6945763
Uthoff J, Nagpal P, Sanchez R, Gross TJ, Lee C, Sieren JC. Differentiation of non-small cell lung cancer and histoplasmosis pulmonary nodules: insights from radiomics model performance compared with clinician observers. Translational Lung Cancer Research. 2019;8(6):979-88. Epub 2020/02/06. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2019.12.19. PubMed PMID: 32010576; PMCID: PMC6976371.
Uthoff JM, Mott SL, Larson J, Neslund-Dudas CM, Schwartz AG, Sieren JC; and the COPDGene Investigators. Computed Tomography Features of Lung Structure Have Utility for Differentiating Malignant and Benign Pulmonary Nodules. Chronic Obstr Pulm Dis. 2022 Apr 29;9(2):154-164. doi: 10.15326/jcopdf.2021.0271. PMID: 35021316.
Philibert R, Dawes K, Moody J, Hoffman R, Sieren JC, Long J. Using Cg05575921 methylation to predict lung cancer risk: a potentially bias-free precision epigenetics approach. Epigenetics. 2022 Aug 3:1-13. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2022.2108082. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35920547.